
RAG Evaluation Lab
RAG Evaluation Lab is an end-to-end workspace I built to help applied ML teams evaluate retrieval-augmented generation pipelines before they reach production. It reduces validation friction by centralizing dataset ingestion, experiment workflows, and performance reporting in one secure environment.
The Challenge
In applied ML environments, validating retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) pipelines before production deployment is critical but operationally complex. Teams must manage diverse document corpora, configure multi-stage pipelines with various parsing/chunking/embedding strategies, execute systematic experiments, and generate decision-ready performance reports. Manual validation workflows create friction, slow iteration cycles, and reduce confidence in production readiness.
The challenge was to build an integrated evaluation platform that could:
- Centralize dataset ingestion and preprocessing workflows
- Configure and orchestrate multi-stage RAG pipeline experiments
- Capture comprehensive telemetry (latency, cost, quality metrics)
- Generate stakeholder-ready performance reports and recommendations
Core Features
1. Pipeline Workbench
Configure parsing, chunking, embedding, retrieval, and judging stages per pipeline with guardrails that keep experiments reproducible and results comparable.
2. Dataset Operations Hub
Drag-and-drop document ingestion with CSV task import support, header alias mapping, and automatic LlamaParse normalization to keep diverse corpora evaluation-ready.
3. Experiment Telemetry
Orchestrated experiment runs capture latency, token usage, cost, groundedness scores, and pass rates so teams see exactly how each pipeline configuration performs.
4. Decision-Ready Reports
Rich dashboards compare pipeline performance, surface recommended configurations, and export Markdown/PDF briefs for stakeholder reviews and production decisions.
High-Level Architecture
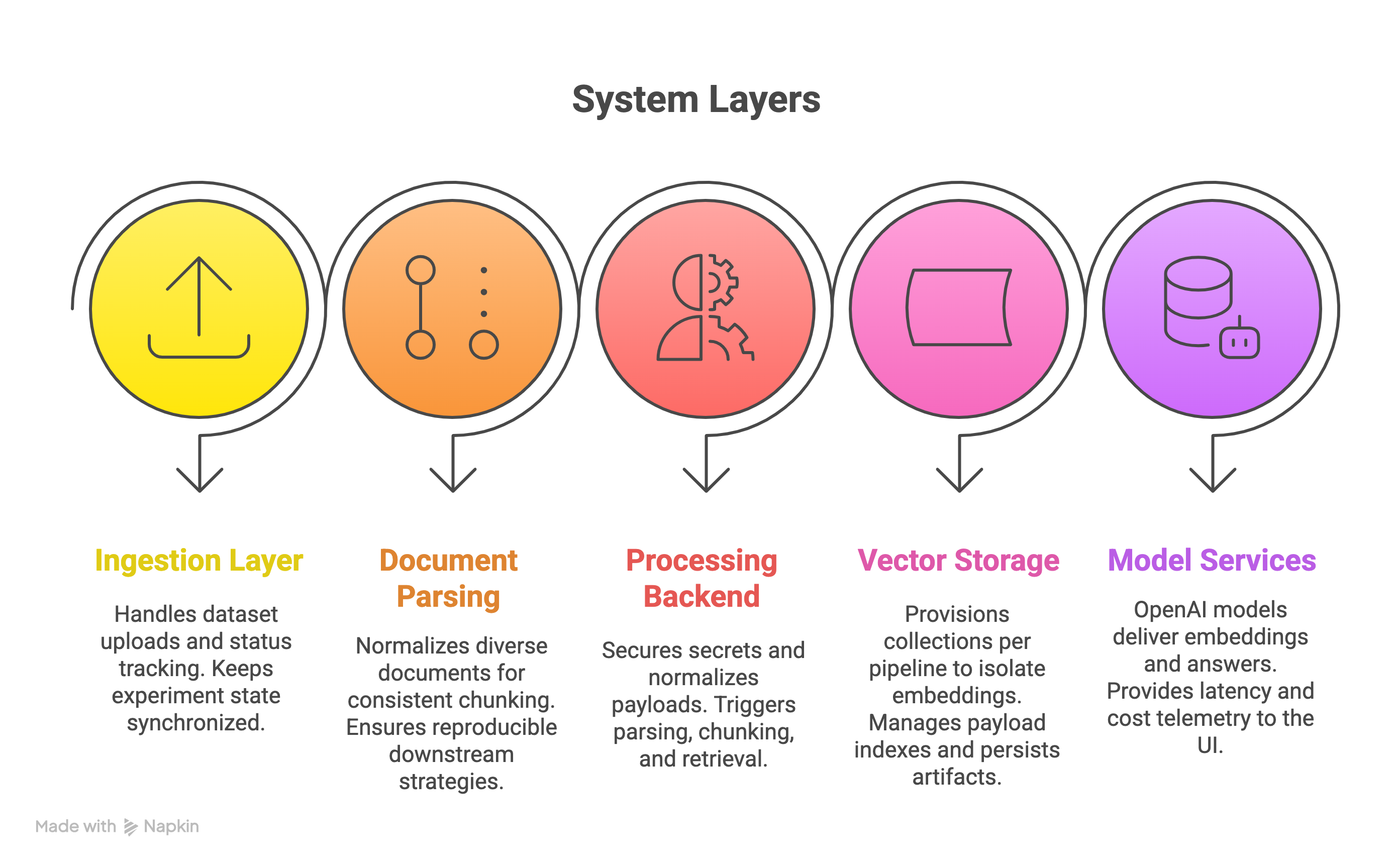
Technical Implementation
Core Technologies:
- Frontend: React + Vite with TypeScript, Tailwind CSS
- Backend: Express.js with Node.js
- Vector Database: Qdrant for pipeline-specific collections
- AI Services: OpenAI for embeddings/completions, LlamaParse for document processing
- Infrastructure: Shared environment loaders, structured logging, automated collection lifecycle management
Key Architecture Decisions:
Platform Architecture – Designed a split TypeScript stack (React/Vite frontend + Express backend) with shared environment configuration, structured logging, and root-level npm scripts to align local development with production workflows.
Backend Integrations – Built typed connectors for OpenAI, Qdrant, and LlamaParse with retry/backoff logic, comprehensive telemetry capture (latency, tokens, spend), and automated Qdrant collection provisioning/cleanup per pipeline to prevent resource leaks.
Frontend Orchestration – Implemented React state providers and context APIs that power dataset ingestion, pipeline configuration, real-time experiment monitoring, and PDF/Markdown report generation while keeping multi-step workflows synchronized.
Experiment Analytics – Automated end-to-end pipeline execution including document parsing, chunking strategy application, vector embedding, retrieval, answer generation, and judge-based scoring to surface groundedness, latency, and cost metrics in decision-ready dashboards.
Results & Impact
Performance Improvements
- 60% reduction in manual evaluation time by automating document parsing, pipeline setup, and experiment execution
- Reproducible judgments across multiple datasets through pipeline-specific vector stores and structured evaluation protocols
- Improved stakeholder confidence with decision-ready dashboards translating technical telemetry into actionable business insights
Operational Benefits
- Centralized validation environment eliminates ad-hoc experiment scripts and manual result tracking
- Consistent evaluation methodology enables reliable pipeline comparison and production readiness assessment
- Exportable reports streamline communication between ML teams and business stakeholders
Key Learnings
-
Document Parsing Trade-offs: Different parsing strategies (layout-aware vs. text-only, chunk size variations) significantly impact retrieval quality. LlamaParse's layout-aware extraction improved recall for structured documents.
-
Modular Pipeline Design: Decoupling parsing, chunking, embedding, and retrieval stages enabled systematic A/B testing and clear attribution of performance differences to specific configuration choices.
-
UX-Backend Alignment: Successful ML tools require tight coupling between workflow UX and backend capabilities. Iterative refinement of configuration interfaces and progress indicators kept users oriented during long-running experiments.
-
Production Readiness Requirements: End-to-end system hardening (API key management, automated cleanup, telemetry hooks, error recovery) proved essential for reliability and maintainability in AI-heavy production environments.
-
Cloud-Aligned Deployment: Designing for cloud deployment patterns (environment-based configuration, containerization readiness, stateless backends) from the start simplified production transitions.